While riding your bike, you must maintain a good posture not only to improve riding efficiency but also to avert any type of injury. Some riders make this seem completely effortless. However, it is not as easy to execute. Although it may seem a bit hard initially, it can definitely be done. And maintaining the correct posture while riding will reward you with many benefits which include a comfortable and efficient ride, improved handling, injury prevention, and effortless breathing.
Along with a good posture, you must also ensure that you have the correct sitting position. This means that your sit bones must be well-positioned on the saddle. When you sit on your bike, your sit bones support your entire body’s weight. Therefore, sit bones can withstand a very good amount of pressure & weight.
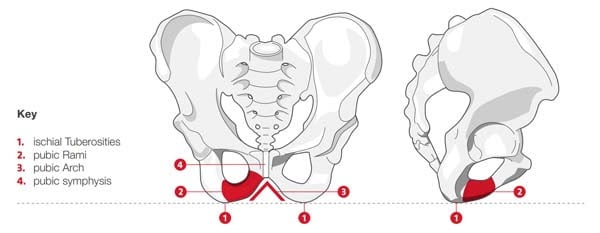
For a typical cycling position, the main areas that lie on the saddle are the pubic arch for women and the perineal area for men. The sitting area is exposed all the way from the top part of the sit bones to the pubic arch and then on to the central perineal area and pubic bone. As men have a much lower pubic arch compared to women, they face higher pressure while riding especially from the saddle’s nose. For more advanced or dynamic riding styles, on which area the rider’s weight is applied is very crucial. Therefore, in such dynamic scenarios, the weight should rest on the pubic bone and the center of the sit bones. The pubic bones and the sit bones converge and form a V-shape. As a result, the more dynamic your sitting position is on the bike, the narrower your bike’s saddle should be. The perfect saddle and saddle width for your body will ensure that your sit bones will rest totally flat on it. This will not only improve your riding efficiency but also remove the pressure from men’s delicate areas and women’s pubic arch.
The diagram given below shows different pelvic positions and which bones are affected by pressure the most for different riding positions.
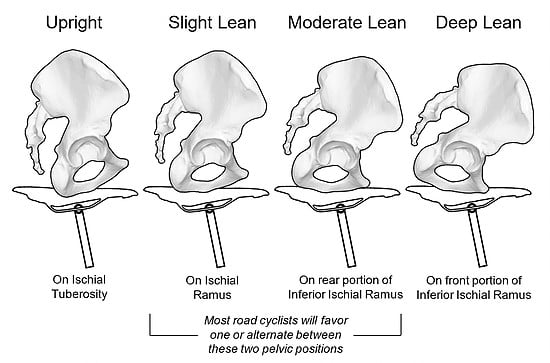
So if you are riding in an upright position, the ischial tuberosity will receive the most pressure. The most common bones affected by pressure is the ischial ramus which receives pressure if you are riding in a moderate lean, a slight lean, and last but not least in a deep lean angled riding position.
1. Riding Positions
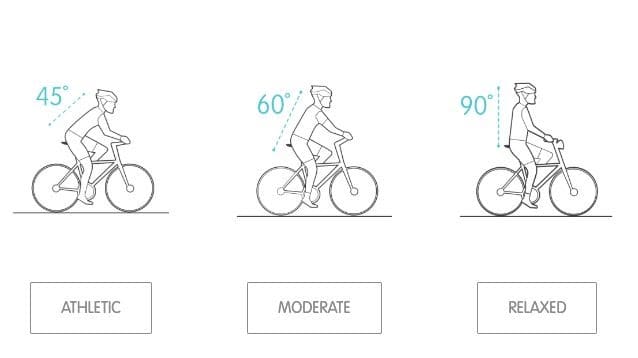
Different riding styles demand different types of sitting positions. Even though a lot of recreational riders and commuters ride while sitting at a 90-degree position, most riders sit on their bikes with a pelvic bend. As a result, all the pressure will not be applied to your sit bones. Now, what position your pelvis will be in depends completely on the riding discipline in question. However, no matter what position your pelvis is in, the guide for accurate measurement of your sit bones to choose a saddle emphasizes a 90-degree angle of the spine.
How you position your body on your bike will determine how your saddle is used. Bicycle saddles come with different kinds of profiles, padding, and saddle widths. All this is done to make sure that you can ride with minimal pressure on your sit bones. You can see the image given below to get a better idea about how to position your body for different types of riding styles.
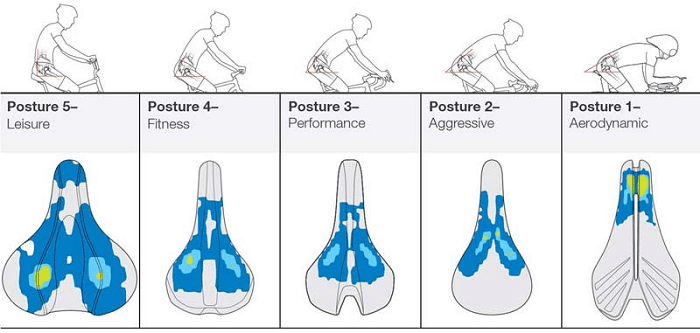
2. Pressure Mapping According to Bike Saddles
To get proper measurements regarding the pressure applied on a saddle when a rider sits on it, a special device is used on the saddle. This device is basically a foil that consists of about one hundred sensors that have the ability to track pressure. This device is planted on the saddle. Therefore, when you sit on the saddle, the pressure is mapped with the sensors and then the outcome is delivered to a computer. As this pressure mapping device uses remote transmitters, the procedure can be carried out anywhere including a lab or even riding out in the real world. Where the pressure is distributed can be tracked easily as the map is colored. In the map, blue color means low pressure. Then as the pressure level increases, the color transforms from turquoise to green, then yellow to orange, and finally to red indicating that it is at maximum pressure.
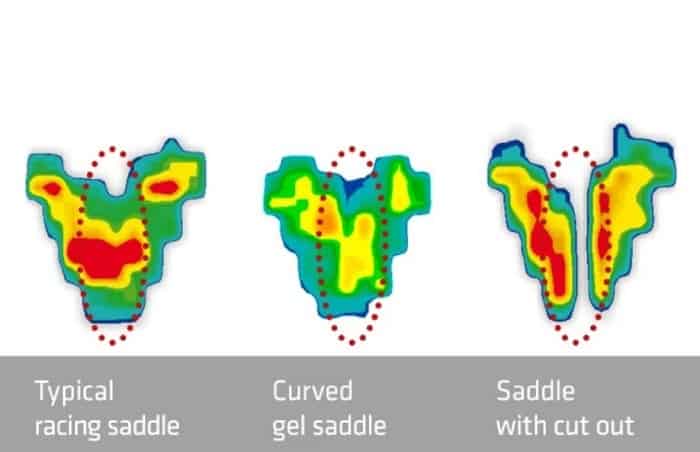
Now let us see the pressure map of different saddle designs.
3. Racing Saddle

If you take a look at the diagram above, the pressure map of a regular racing saddle shows an ideal allocation of pressure when a rider sits on it. This is because the map shows the color red on the sit bones area and yellow or orange color in the pubic bones area. This indicates that these areas are receiving maximum pressure and the perineal area is getting almost no pressure at all.
4. Curved Gel Saddle

The curved gel saddle pressure map shows that there is a good amount of pressure being applied to the perineal area and the pubic bone arch area. As the perineal area is a sensitive place, a high amount of pressure in that area is not good for the rider and can lead to injuries.
5. Gel Saddle With a Cut-out Section

The pressure map of this type of saddle is quite alarming. As you can see it indicates that a high amount of pressure is applied on the edges of the perineal area. The perennial area consists of vital nerves and arteries and therefore is a risky area to receive so much pressure. Even the blood flow will not be affected much, riding on this type of saddle can still lead to numbness.
➥ Some saddles are designed to face perineal numbness from cycling. You can get the saddles here: bike seats that protect the perineum.
6. Saddle Geometry
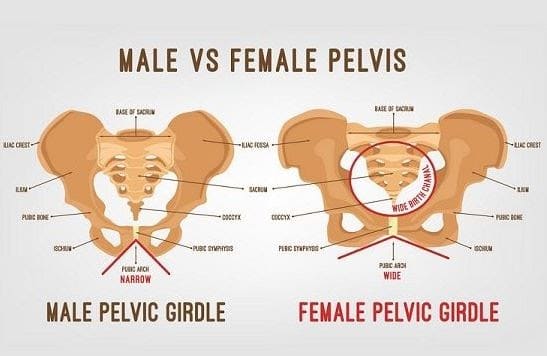
A man’s pelvis is quite distinct from that of a woman’s and the main reason for this is that a woman’s pelvis is required to enable childbirth. You can clearly see this in the diagram given above. After conducting our own research and reading the work of various renowned organizations we have found that for men, the sit bone distance is about 6 – 16 centimeters, and for women about 9 – 17 centimeters.
Before, while riding a bike women had to endure more pressure due to the saddle nose at the lower part of the pubic bone arch. This is because a lot of women have small sit bone distances while a lot of men can have big sit bone distances. Therefore, women and men do not require different saddles anymore. A lower saddle nose can remove any type of pressure from a man’s perennial area and moving it 2 centimeters forward from the female pubic bone position can fix the high-pressure issue as well.
You can learn more about the differences between the pelvis of a man and a women by taking a quick look at the table below:
| # SL | Male Pelvis | Female Pelvis |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The male pelvis is small & narrow. It consists of thick & heavy bone. | The female pelvis is wide & big. It consists of thin & light bone. |
| 2 | It can support heavier bodies due to its strong structure of muscle groups. | It has the purpose of childbearing. |
| 3 | Men have a deep pelvis. | Women have a shallow pelvis. |
| 4 | The arch is V-shaped with an angle that is less than 90°. | The arch is wide with an angle that is greater than 90°. |
| 5 | The outlet is narrow. | The outlet is wide. |
| 6 | The sacrum is curved, long & narrow. | The sacrum is curved, short & wide. |
| 7 | It has a longer Ischial tuberosity. | It has a shorter Ischial tuberosity. |
7. Pain During Your Rides
Pain is often caused due to excessive pressure. This pressure can be relieved with a larger area. As we all know, the area is larger, the pressure will be lower.
Another cause for the pain can be a saddle which is a bit too soft. This type of saddle tends to feel highly uncomfortable after riding on it for about only 30 to 40 minutes.
Then the sit bones drop in too far into the padding and your muscles become irritated. And that is when the pain starts. For men, this adds pressure to the perineal area. As for women, they feel much more pressure at the lower pubic bone arch. Some types of soft paddings even tend to reduce the blood flow during riding sessions.
8. Industry Research
A lot of research is conducted in the cycling industry to find the ideal saddle shape while taking the differences between men’s and women’s riding positions into consideration. One, in particular, that is very interesting is about sit bones width for optimal riding positions upon variations in ischial variations.
The brand Selle researched with about 240 participants and discovered a variety of sit bone widths. With these results, they produced three saddle widths. These widths were evaluated at a spring angle of 90 degrees. The findings of this research state that because of the v-shape of the pelvic, the sit bone or Ischial distance depends on the riding position. Therefore, as the spring angle lowers or inclines, the distance will also get smaller. You can see this clearly, in the images given below.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Why Do I Get Saddle Discomfort?
Ans.: One of the major reasons for getting saddle discomfort is an improper bike fit. You could be feeling pain or discomfort because of your saddle being too forward, backward, higher than you require, or even lower. Therefore, you should ensure that your saddle height is correct and it is in the right position according to the pedals. You can watch the video linked below to learn how to do this properly:
➥ If you ride for a short time and for recreational purposes, gel bike saddles or gel seat covers can remove your discomfort immediately.
Q2. Where should I sit on my bike saddle?
Ans.: Finding the ideal position on your bike saddle is very important to experience a comfortable ride. To do this, you should sit on the widest part of the saddle which is the furthest away at the back. Also, you should lean the front part of the saddle by just a little bit. This will allow you to remove pressure from your sit bones and also reduce the chances of numbness.
Q3. Should I be able to touch the ground when sitting on my bike?
Ans.: The saddle height is crucial for you to find a highly comfortable and safe riding position. While sitting on your bike, the arch of your feet should be able to touch the ground. With that being said, it is important to note that if you can put your feet flat onto the ground then your saddle height is quite low and you should increase it. Also, if you can touch the ground only with your toes then your saddle height is too high and you should lower it.
➥ Read more on perfect saddle fitting: Bike Saddle Fit Guide: 6 Images will Make the Differences.
Q4. How important is the standover height?
Ans.: It is very important. You might hurt yourself when you suddenly stop your bike if you cannot stand over your bike’s top tube without coming in contact with it. The risk of an accident occurring is very high if the height of the top tube is higher than you are. So make sure you check your bike’s top tube height before taking it out for a ride.
Q5. What happens if my saddle is too high?
Ans.: As mentioned before, if you want to enjoy a smooth and comfortable ride on your bike, your saddle needs to be at the right height. If the saddle is too high, you will most likely feel a slight pressure at the back part of your knee. You may also observe that you feel wobbly while riding on the bike. You will not be able to pedal efficiently either. Also, if the saddle is too low, you’ll feel discomfort, especially at the knees. So make sure your saddle is not too high and not too low either.
➥ Read more on this saddle height topic: Comparison between Mountain Bike vs Road Seat Height.
Conclusion
We hope you got all your questions answered by reading our article. We always strive to provide you with the latest information in the hope that it may enrich your cycling lives and bring you closer to your goals. Sitting in the correct position on the right saddle can boost your performance and also help to keep you safe from injuries and other health concerns. So thank you for reading this article. Ride safely!

I’m surprise about the answer given about that I should touch the ground with my feet arch. It is imposible to touch the ground if my bike is fitted correctly. That is something that I performed many time to bike riders. I really don’t understand your answer to the person that is asking. Can you clarify this for the benefit of your readers?